Welcome friends thank you for coming to this content today we will be covering 42 most asked Cisco CCNA interview questions and answers first we will be covering.
Cisco CCNA interview questions and answers on OSI Model & TCP/IP
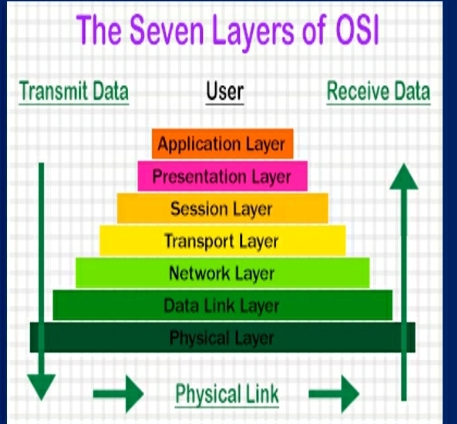
OSI Model is a reference model which shows how an application communicates in a network, it consist of 7 layers
Layer 1 - Physical Layer (It sets up bit-streams across a network)
Layer 2 - Data Link Layer (It set up links across a physical network)
Layer 3 - Network Layer (It handles addressing & routing data)
Layer 4 - Transport Layer (Used for an end to end communication)
Layer 5 - Session Layer (Used to interhost communicate)
Layer 6 - Presentation Layer (for data representation & encryption)
Layer 7 - Application Layer (Used to process application)
Question 2 Explain TCP/IP model with OSI Model
- TCP/IP has 4 layers and OSI Model has 7 layers
- The upper most of layer (4th Application layer) of TCP/IP Model has similar function as OSI Model's upper layer (7th Application, 6th Presentation and 5th Session layer)
- 3rd Transport layer in TCP/IP is similar to 4th Transport layer in OSI Model.
- 2nd Internet layer in TCP/IP Model is 3rd Network layer in OSI Model.
- Lower layer Network layer in TCP/IP has similar functions as OSI Model lower 2 layer ( Physical layer and Data link layer )
As data is passed from the user application down the virtual layer of the OSI Model, each layer adds a header containing protocol information specific to data layer. These header are called protocol data units (PDUs) and the process to adding these headers is called encapsulation.
For example
- Transport layer protocol (TCP) will add a header containing flow control, Port number and sequencing.
- The Network layer header contains logical addressing information.
CCNA Interview Question and Answer on Topology & Ethernet
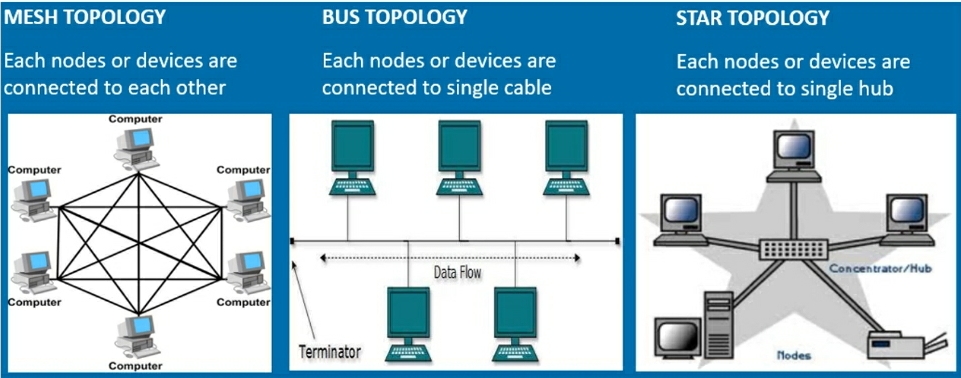
In network we have mainly three topology
1. Mesh Topology
2. Bus Topology
3. Star Topology
Question 5 What is ethernet? Explain different cabling type
Ethernet is a suite technology which provides data-link and physical specification for controlling access to a shared network medium.
Ethernet can be deployed over three types of cabling.
- Cat3- three twists per inch.
Question 7 Explain an ethernet frame
- The absolute minimum frame size for Ethernet is 64 bytes ( or 512 bits ) including headers.
- A frame that is smaller than 64 bytes will be discarded as a runt.
- The required fields in an Ethernet header add up to 18 bytes - thus , the frame payload must be a minimum of 46 bytes , to equal the minimum 64 - byte frame size.
- If the optional 4 - byte 802.1Q tag is used , the Ethernet header size will total 22 bytes , requiring a minimum payload of 42 bytes.
- By default , the maximum frame size for Ethernet is 1518 bytes – 18 bytes of header fields , and 1500 bytes of payload - or 1522 bytes with the 802.1Q tag.
- A frame that is larger than the maximum will be discarded as a giant.
CCNA Interview question and answers on Hub, Switch & Router
Question 8 What is a difference between Repeaters, Hub, Bridge and Switch
Repeaters are the most basic form of forwarding devices . A repeater receives a frame , regenerates an exact copy of the frame and forwards it along its way . They have two ports : an input port and an output port.
Hubs are multiport repeaters . Whereas a repeater will have two ports ( one in , one out ) , a hub has 24 or more ports . A signal is delivered to any port is regenerated and forwarded out all ports.
A bridge is a different than a repeater or a hub because it can examine frames . The ability to read MAC addresses gives it the ability to make intelligent decisions about forwarding packets .
Switches are similar to bridges . Switches assist packet forwarding by creating a collision domain on each switched port . A table is built containing this map , which allows the switch to forward traffic only to the port attached to the destination node.
Question 9 Explain MAC Address table in ethernet switches
Ethernet switches build MAC address tables through a dynamic learning process. The switch will build the MAC address table by checking the source MAC address of each frame.
In this example:-
Question 10 Explain Collision Domain and Broadcast Domain
 |
Multilayer switching refers to any switch that forwards traffic at layers higher than Layer 2 . A Layer 3 switch is considered as a multilayer switch, as it forwards frames at Layer 2 and packets at Layer 3.
A Layer - 4 switch provides the same functions as a Layer - 3 switch , but will also examine and cache Transport 4th OSI layer application flow information , such as the TCP or UDP port
Question 12 What is the STP (Spanning tree protocol).
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) runs on Layer 2 of OSI Model which runs on bridges and switches. The main function of STP is to ensure that no loops are created when there are redundant paths in your network . A failure of your primary link activates the backup links so that users can continue to use the network. Without Spanning Tree Protocol on the bridges and switches, the failure can result in a loop.
Spanning Tree Protocol creates a tree that spans all the switches in an extended network . STP switches exchange Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDU's) to build the topology database. BPDU's are forwarded out all ports every two seconds.
STP topology gets build in a multistep convergence process :
• A Root Bridge is selected
• Root ports are identified
• Designated ports are selected
• Ports are placed in a blocking state , to eliminate loops
Question 13 What are the commands to check cisco switch basic configuration.
CCNA interview questions answers on Switch or VLANs
Question 16 What are types of VLAN ports?
To configure an interface as a access port:
To manually configure an interface as a trunk port:
CCNA interview questions answers on VTP
Question 19 What is VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP)?
VLAN Trunk Protocol reduces administration in a switched network. When you configure a new VLAN on one VTP server, the VLAN is distributed through all switches in the domain which reduces the need to configure the same VLAN everywhere.
VTP requires that all switches join a VTP domain. Switches must belong to the same domain to share VLAN information.
Question 20 Explain different modes of VTP?
VTP has three modes as below
1. SERVER MODE
Full control over VLAN creations and modifications for their domains.
2. CLIENT MODE
VTP clients do not allow the administrator to create, change or delete any VLAN's; instead they listen to the VTP's advertisements from other switches and modify their VLAN configuration accordingly.
3. TRANSPARENT MODE
VTP transparent mode switches will not participate in VTP advertisements. It can create and delete VLAN's that are local only to itself. It will not propagate to other switches, and will not advertise own VLAN configuration
Question 21 What are the commands to configure VTP?
Below are the commands to configure VTP
Switch(config)# vtp mode server
Switch(config)# vtp mode client
Switch(config)# vtp mode transparent
Świtch(config)# vtp password ABC123 -----Password
Question 23 What is VTP Pruning?
Switches belong to only one broadcast domain. A Layer 2 switch forward both broadcasts and multicasts out every port in the same VLAN.
This sends out broadcasts out trunk ports to other switches, which will in turn flood that broadcast out all ports in the same VLAN.
VTP pruning stops unnecessary broadcast or multicast traffic in switching infrastructure.
CCNA Interviews questions and answers on IP address & NAT
Question 24 Explain IP Address & Subnet Mask
What is the IP Address:
IP Address is a decimal 32 bit structure which provides logical addressing for hosts. An IP address helps identify a host, and what network that host exists on. An IP address is comprised of four octets, separated by periods. Each octet is an 8-bit number, resulting in a 32-bit IP address.
IP provides two fundamental Network layer services:
1. Logical addressing - provides a unique address that identifies both the host, and the network
2. Routing - determines the best path to a particular destination Network
What is the Subnet Mask
Part of an IP address identifies the network. The other part of the address identifies the host. A subnet mask is required to provide this distinction: Example 255.255.255.0
Question 25 Explain Public vs Private IP Address
A private address is for internal use within a home or organization, and can be freely used by anyone. Private addresses can never be routed on the Internet. In fact, Internet routers are configured to immediately drop traffic with private addresses.
Three private address ranges class.
A public address can be routed on the Internet. It must be Internet accessible must be configured with reachability from outside world. Allocation of public addresses is governed by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA).
• Class A - 10.x.x.x /8
• Class B - 172.16.x.x /12
• Class C - 192.168.x.x /24
Question 26 What is Network Address Translation (NAT)?
Network Address Translation (NAT)
NAT allows a host configured with a private address to be stamped with a public address, it allows that host to communicate across the Internet.
It is possible to translate multiple privately-addressed hosts to a single public address, which conserves the public address space
Question 27 Explain different Types of NAT
NAT can be implemented using one of three methods
Static NAT - It performs a static one on one translation between two addresses, or between a port on one address to a port on another address. Static NAT is mostly used to assign a public address to a device behind a NAT featured firewall or router.
Dynamic NAT – It utilizes a pool of global addresses to dynamically translate the outbound traffic of clients behind a NAT-enabled device.
NAT Overload or Port Address Translation (PAT) - translates the outbound traffic of clients to unique port numbers of a single global address. PAT is important when the number of internal clients exceeds available global addresses.
CCNA Interview question and answers on Subnetting
Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) is a method of representing a subnet mask. CIDR identifies the number of binary bits set to a 1 (or on) in a subnet mask
- A network using its default subnet mask is termed to as a classful network.
- A networking using subnetting in subnet mask is referred to Classless network.
Question 29 Explain Subnetting
Subnetting is the process of creating new networks (or subnets) by stealing bits from the host portion of a subnet mask.
Stealing bits from hosts creates more networks but fewer hosts per network.
Consider the following Class C network
This single network can be segmented, or subnetted, into multiple networks.
CCNA interview question and answers on ARP, TCP/UDP
Address Resolution protocol (ARP)
ARP allows a host to determine the MAC address for particular destination IP address.
Question 31 Explain UDP & TCP Protocol
TCP & UDP are part of The Transport layer (OSI Layer 4), This layer is responsible for the reliable transfer of data, by ensuring that data arrives at its destination error-free and in order.
Transport layer communication falls under two categories:
O Connectionless (UDP) - requires no connection before data is sent. Connection-oriented protocols provide several important services:
O Connection-oriented (TCP) – requires that a connection with specific agreed-upon parameters be established before data is sent.
- Connection establishment - connections are established, maintained, and ultimately terminated between devices.
- Segmentation and sequencing - data is segmented into smaller pieces for transport. Each segment is assigned a sequence number, so that the receiving device can reassemble the data on arrival.
- Acknowledgments - receipt of data is confirmed through the use of acknowledgments. If a segment is lost, data can be retransmitted to guarantee delivery.
- Flow control (or windowing) - data transfer rate is negotiated to prevent congestion
Question 32 list important TCP/UDP port no
Question 33 Explain TCP Three-Way Handshake
TCP forms three-way handshake to setup a TCP connection. Control messages are passed between the two hosts as the connection is set up:
• Host A sends a SYN (short for synchronize) message to Host B to initiate a connection.
• Host B responds with an ACK (short for acknowledgement) to Host A's SYN message, and sends its own SYN message. The two messages are combined to form a single SYN+ACK message.
• Host A completes the three-way handshake by sending an ACK to Host B's SYN.
Question 34 Explain IPV6 Address
The IPV6 Address :
The IPV6 address is 128 bits, as opposed to the 32-bit IPV4 address. Also unlike IPV4, the IPV6 address is represented in hexadecimal notation, separate by colons.
An example of an IPV6 address would be.
1254:1532:26B1:CC14:0123:1111:2222:3333
Each “grouping" (from here on called fields) of hexadecimal digits is 16 bits, with a total of eight fields.
CCNA interview question and answers on Routing
Question 35 explain difference between IGP and EGP protocol
Question 36 What is difference between static and dynamic routing?
Question 37 What is the default AD values of routing protocol?
Question 38 What is RIB and FIB in Routing Table?
FIB is the Forwarding Table
FIB contains destinations and the interfaces to get to those destinations. It is used by the router to figure out where to send the packet.
RIB is the Routing Table
RIB contains a list of all the destinations and the various next hops used to get to those destinations. One destination can have lots of possible next hops but only the best next-hop goes into the FIB.
Question 39 What are the advantage & disadvantage of OSPF?Question 40 What is Loopback interface in cisco router?
LOOPBACK INTERFACE- is a logical interface in cisco router, This interface is not a physical interface like Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Interface in Cisco router.
They are used as termination points for remote source-route bridging (RSRB) and data link switching plus (DLSW+), This virtual interface is always up even if physical interface is down.
Loopback interface is used to emulate a physical interface, by default cisco router doesn't have loopback interface it needs to be created using below command:
Question 41 What is CDP (cisco Discovery Protocol)?
CDP is Cisco discovery protocol which is cisco proprietary. It is used to share information about other directly connected Cisco equipment's.
- It is a layer 2 Data link layer protocol.
- It works based on MAC addresses (device hardware address).
- It is used to find adjacent connected Cisco devices.
- IP addresses,
- Port numbers,
- IOS details,
- Router models.
HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) is redundant protocol developed by Cisco to provide gateway level redundancy without performing any additional configuration on end devices in network.
HSRP Active and Standby routers send hello packets for communication over UDP protocol. These hello messages are forward to multicast address 224.0.0.2 to communicate between routers in HSRP.
HSRP provides backup to a router in the event of failure.
 Reviewed by YourOnlineZone
on
30 June
Rating:
Reviewed by YourOnlineZone
on
30 June
Rating: