Explain Open Shortest Path First Protocol
- OSPF stand for open shortest path first.
- OSPF use two type of multicast address 224.0.0.5 and 244.0.0.6
- Standard Protocol.
- Its link start protocol.
- It is use (shortest path first) or dikistra Algorithm.
- Unlimited hop count.
- Metric is cost (cost=10^8/B.W)
- It Administrative distance value is 110.
- It is classless routing protocol.
- It support VLSM and CIDR.
- It support only equal cost load balancing.
- Introduce the concept of Area to ease management and control traffic.
Explain Seven state of OSPF protocol
1. Down state
2. Init state
3. 2 Way state
4. Extart state
5. Exchange state
6. loading state
7. Full state
Has been explained OSPF Protocol state
- Dawn State
- Init State
This state specifies that the router has received a hello packet from its neighbor. But the receiving routers ID was not included in the hello packet. When a router receives a hello packet from a neighbor, it should list the sender router ID in its hello packet as an acknowledgment that is received a vailed hello packet.
- Two-Way State
In the 2-way state with all other neighbor. On
Point-to-Point and Point-to-multipoint network. A router become full with all connected router.
At the on of this stage, the DR and BDR for broadcast and non-broadcast multi-access networks are elected. For more information on the DR election process, refer to DR election.
- Exstart State
In this start the
router and their DR establish a master-slave relationship and choose the
initial sequence number for adjacency formation. The router with the higher
router ID become the master and starts the exchange, and as such, is the only
router that can increment the sequence number. Note that would logically
conclude that the DR/BDR with the highest router ID will become the master
during this protocol master-salve relation.
- Exchange State
In the exchange state, OSPF router exchange database descriptor (DBD) packets. Database descriptors contain link-state advertisement (LSA) headers only and describe the contains of the entire link-state database. Each DBD packet has a sequence number which can be incremented only by master which is explicitly acknowledged.
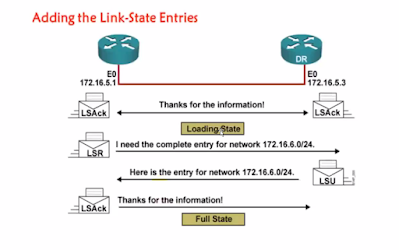
- Loading State
In this state, the actual exchange of link state information occurs. Based on the information provided by the DBDs, router send link-state request packets. The neighbor then provides the requested link-state update packets. During the adjacency, if a router receives an outdated or missing LSA, it request that LSA, it request that LSA by sending a link-state update packets are acknowledged.
- Full State
In this state. Router are fully adjacent with each other .All the router and network LSAs are exchanged and the router database are fully synchronized.
Type of OSPF Protocol Table
1. Neighbor Table
Also known
that adjacency database
Contains
list of directly connected router ( neighbor )
Router#show ip
ospf neighbor
2. Database Table
Typically referred to as LSDB (link-state-database)
Contains information all the possible router to the
network with in the area
Router#show ip ospf database
3. Routing Table
Contains list of best path to each
destination
Router#show ip routh
Explain OSPF Protocol work in Area
1. Backbone area :- Area 0 is always called backbone area. The task of backbone area is to transmit routing information in other area and the routing is called inter area routing.
2. Off backbone area :- The area configured 1 to 65535 off backbone area and the routing information is called inter routing these area must be connected area 0 to communicate other area.
3. Stub Area :- Any area which has only one exit point to transmit information is called setup area. Mostly 0 is stub area.
ABR :- Any router which connects any area 0 to another area is called ABR (Area Border Router)
A Router connected with two different areas is known as an area border router. Suppose one interface of a router connects with area 0 and another interface connects with area 1 then this type of router is known as an area border router.
ASBR (Autonomous system boundary router):- Router which connect on AS to other AS is called ASBR (Autonomous system boundary router)
A Router connected with two different areas is known as an area border router. Suppose one interface of a router connects with area 0 and another interface connects with area 1 then this type of router is known as an area border router.
Explained OSPF Protocol Terminology
- Link
- RID
- Neighbour
- Adjencey
- Hello Packet
- LSU
- Neighbourship Database
- Designated Router
- Backup Designated Router
Any router interface the network configure whit OSPF protocol that is know as link.
2. RID ( Router identifier ) Terminology
The ip address of any interface of router through which router identifier in the network is called router ID.
3. Neighbour Terminology
Directly connected router I the network is called neighbour.
4. Adjencey Terminology
The sharing of routh between the router is called Adjencey.
5. Hello Packet Terminology
The packet that are send by router to discover neighbor in the network is called hello packet this hello packet non as link state advertisement. If you are connected to multi network point-two-point link.
6. LSU Terminology
LSU stand for link state whenever there is any called update timer in every 30 min.
7. Neighboruship Database Terminology
The list of OSPF router for which the hello packet is acknowledge and store in neighboruship. In other word we can say that in neighboruship database available information about neighboruship.
8. Designated router Terminology
The Router which has highest router ID is called designated router. It will utilize the link on proprietary for multicast by using 224.0.0.6 ip address.
9. Backup Designated router Terminology
The router has alternate best router ID or RID is called BDR.
How to configure Single area of OSPF routing protocol
Configuration Command Of OSPF Protocol
Router1(Config)#router
ospf 100 (process id)
Router1(Config)#net
11.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router1(Config)#net
10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router2(Config)#router
ospf 100 (process id)
Router2(Config)#net
11.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router2(Config)#net
20.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router2(Config)#net
12.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router3(Config)#router
ospf 100 (process id)
Router3(Config)#net
12.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Router3(Config)#net
30.0.0.0 0.255.255.255 area 0
Note:-
What is process id of OSPF
processes were being run on the same device
What is Wildcard mask
 Reviewed by YourOnlineZone
on
03 May
Rating:
Reviewed by YourOnlineZone
on
03 May
Rating: